OpenAI released an announcement on February 13, 2026, announcing the addition of advanced security settings for ChatGPT.
OpenAI states that as AI systems begin to take on more complex tasks, especially in scenarios involving web pages and external applications, security risks are surging. One emerging and prominent risk is “prompt injection.” In this type of attack, a third party misleads the AI with prompts to execute malicious commands or induce it to disclose sensitive internal information.
To help users and organizations mitigate the risk of tooltip injection attacks, OpenAI has announced two new protective measures, summarized as follows:
-
One is ChatGPT’s “Lockdown Mode,” an optional advanced security setting for high-risk users;
-
Secondly, for capabilities that may introduce additional risks, a new “Elevated Risk” label has been added to ChatGPT, ChatGPT Atlas, and Codex.
OpenAI states that these new measures build upon its existing multi-layered protection, including sandbox mechanisms, protection against URL-based data breaches, monitoring and enforcement mechanisms, and enterprise-level controls such as role-based access control and audit logs.
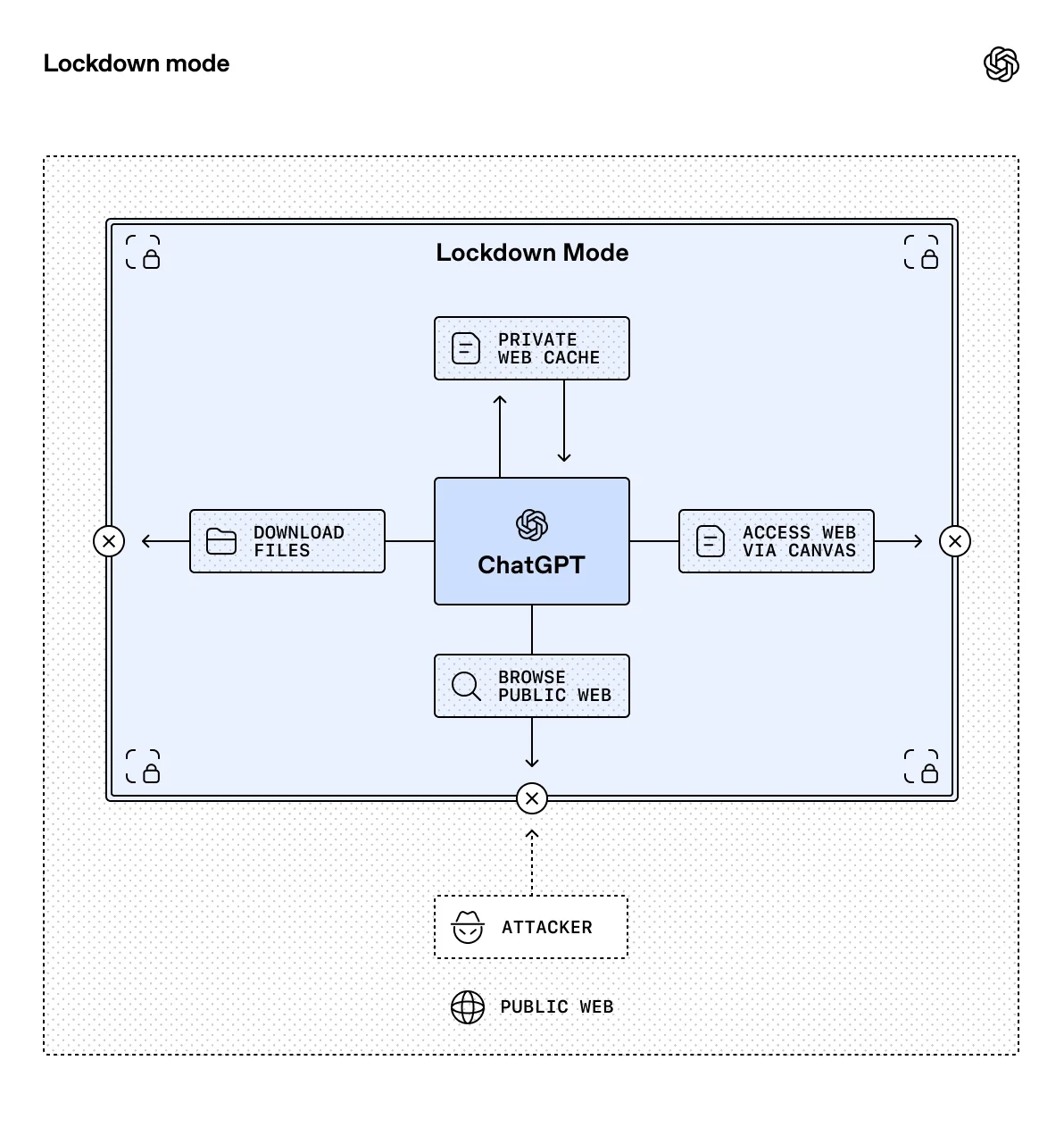
Lockout mode is an optional advanced security setting primarily aimed at a small group of users who highly value security, such as executives or security teams in large organizations, to enhance their ability to protect against advanced threats.
OpenAI emphasizes that most users do not need to enable lockout mode. Its core objective is to reduce the risk of data leakage caused by attacks such as message injection by strictly limiting ChatGPT’s interaction with external systems.
OpenAI stated that the locked mode will deterministically disable certain tools and capabilities in ChatGPT that could be exploited by attackers, thereby preventing attackers from leaking sensitive data from user conversations or connected applications through methods such as prompt injection.
As an example, OpenAI mentions that in locked mode, ChatGPT’s web browsing functionality will be restricted to accessing only cached content. This restriction aims to prevent sensitive data from being obtained or leaked by attackers during browsing. For certain functions that cannot provide strong deterministic data security guarantees, locked mode will completely disable them.
OpenAI also points out that the commercial subscription version of ChatGPT already offers enterprise-grade data security capabilities, and Lockdown Mode is a further enhancement on top of that. This mode is currently available for ChatGPT Enterprise, ChatGPT Edu, ChatGPT for Healthcare, and ChatGPT for Teachers. Administrators can enable Lockdown Mode by creating a new role in Workspace Settings. Once enabled, Lockdown Mode adds additional restrictions on top of existing administrator settings.
Since some critical tasks still rely on external applications, OpenAI says Workspace administrators will still have more granular control: administrators can precisely select which applications, and within those applications, specific operations, can be made available to users in locked mode.
OpenAI also mentioned that, in addition to Lockout Mode, its Compliance API Logs Platform provides more detailed visibility into application usage, shared data, and connection sources, helping administrators maintain oversight and auditing capabilities. OpenAI stated that it plans to make Lockout Mode available to consumer users in the coming months.
Regarding risk labeling, OpenAI stated that AI products are often more helpful when connected to applications and websites, and the company is investing heavily in protecting the security of connected data. However, at the same time, some network-related capabilities introduce new risks that have not yet been fully addressed by existing industry security and protection measures. OpenAI believes that some users may be willing to take these risks, so it is important to allow users to decide for themselves whether and how to use these capabilities, especially when dealing with personal and private data.
OpenAI states that its approach is to provide usage guidelines within its products for features that may introduce additional risks. To make these guidelines clearer and more consistent, the company is standardizing the labeling of a small subset of existing capabilities. These features will be presented with a unified “Elevated Risk” label in ChatGPT, ChatGPT Atlas, and Codex, ensuring users receive consistent feedback when encountering similar capabilities across different products.
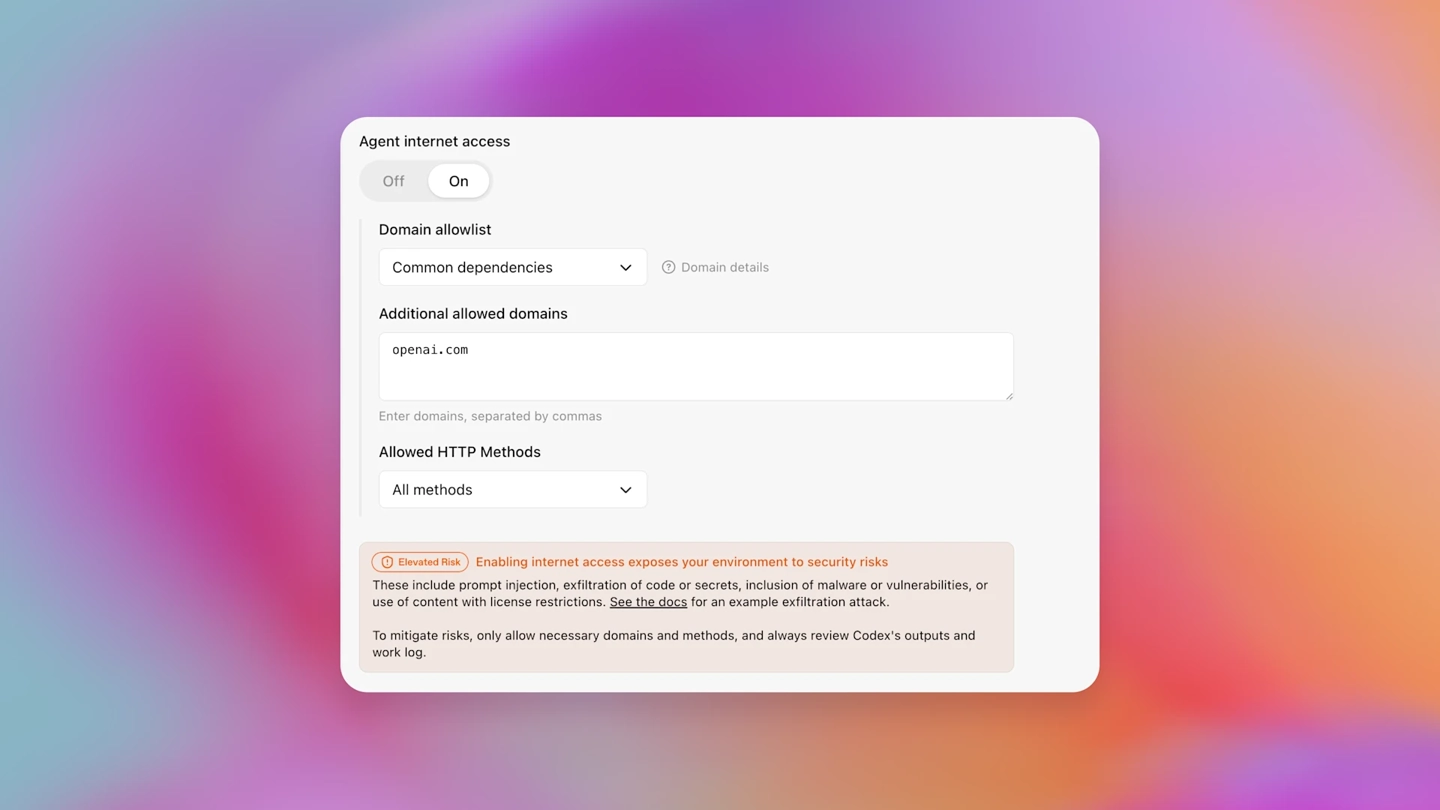
OpenAI cited Codex as an example, stating that in its programming assistant product, developers can grant Codex network access, enabling it to perform operations such as viewing documents on a webpage. However, the relevant settings interface will display an “Increased Risk” label, providing clear explanations, including what changes will occur after enabling it, what risks might be introduced, and when it is appropriate to enable this access permission.